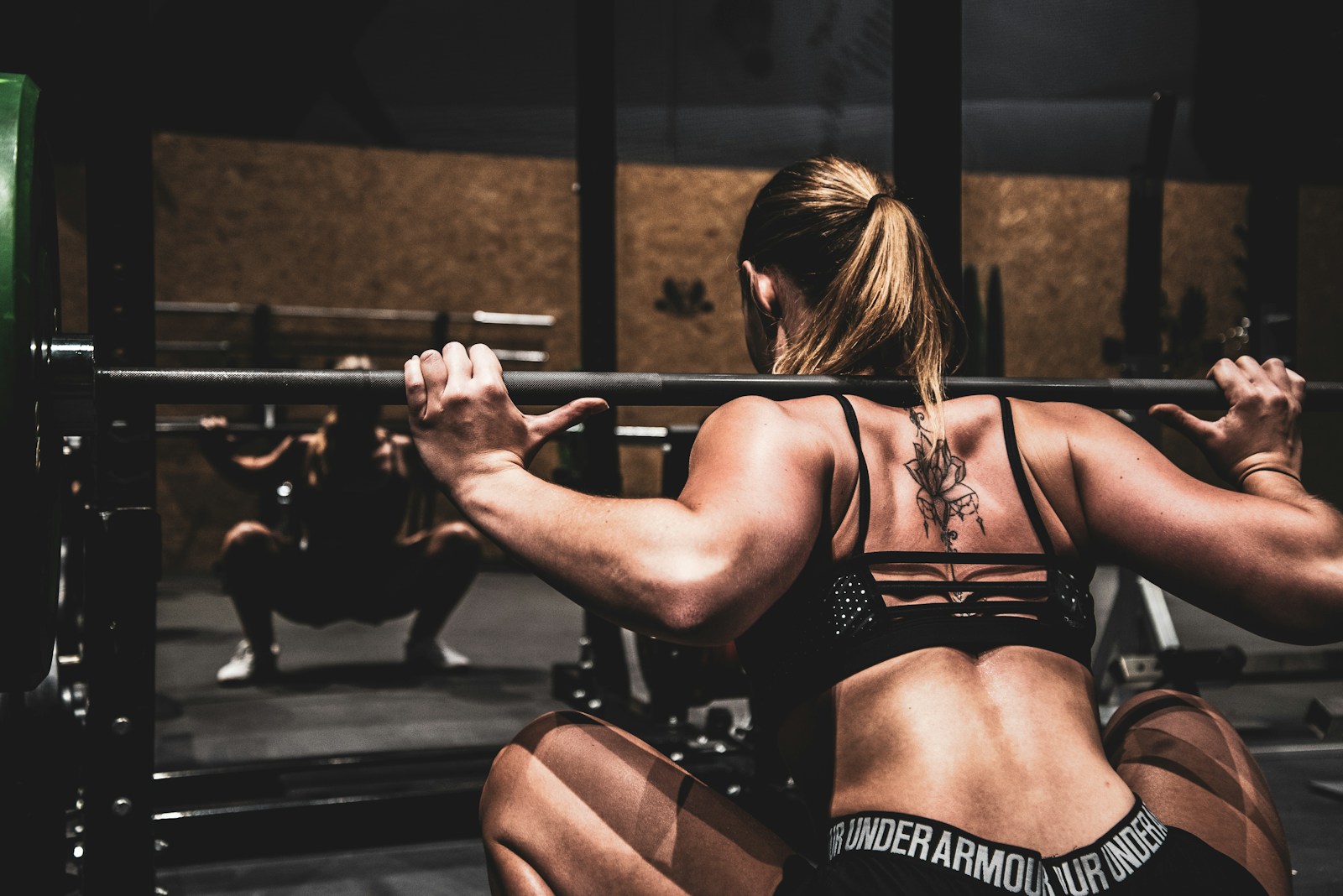
 Building a more prominent and well-shaped butt is a goal for many fitness enthusiasts, which is achievable through targeted exercises, proper nutrition, and rest. Engaging in a consistent workout regimen that focuses on the gluteal muscles, the primary trio that makes up the buttocks, can lead to significant improvements in shape, strength, and size. The gluteal muscles consist of the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus, and each plays a role in the overall appearance and function of the buttocks.
Building a more prominent and well-shaped butt is a goal for many fitness enthusiasts, which is achievable through targeted exercises, proper nutrition, and rest. Engaging in a consistent workout regimen that focuses on the gluteal muscles, the primary trio that makes up the buttocks, can lead to significant improvements in shape, strength, and size. The gluteal muscles consist of the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus, and each plays a role in the overall appearance and function of the buttocks.
In conjunction with exercise, nutritional intake makes a critical difference in muscle growth and recovery. Consuming an adequate amount of proteins, balanced with carbs and healthy fats, supports muscle repair and growth, thus contributing to a bigger butt. Additionally, incorporating rest days and recovery techniques helps to prevent overtraining and allows the muscles to rebuild stronger than before.
Key Takeaways
- Consistent targeted exercise is key for developing the gluteal muscles.
- Proper nutrition supports muscle growth and recovery.
- Adequate rest is essential to prevent overtraining and promote muscle repair.
Understanding the Gluteal Muscles
The gluteal region, commonly referred to as the booty, encompasses three primary muscles: the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus. They are integral to various movements and maintaining proper posture.
Anatomy of the Glutes
The gluteus maximus is the most prominent and superficial of the gluteal muscles, renowned for its power and size. It originates from the pelvis and sacrum and inserts into the femur and iliotibial tract. The gluteus medius lies beneath the maximus and is critical for abduction and rotation of the hip. Finally, the gluteus minimus, the smallest of the trio, also plays a role in hip stabilization and abduction.
- Gluteus Maximus: Largest muscle in the gluteal region, responsible for hip extension, outward rotation, and maintaining the extended knee.
- Gluteus Medius: Primarily stabilizes the hip and pelvis, particularly during activities like walking or running.
- Gluteus Minimus: Works in conjunction with the medius to stabilize and abduct the hip.
Role in Movement and Posture
The gluteal muscles are not only crucial for movement but also for posture. The gluteus maximus is essential for rising from a seated position, climbing stairs, and maintaining an upright posture. It is the powerhouse that propels the body forward during walking or running. Meanwhile, the gluteus medius and minimus prevent the pelvis from dropping to the opposite side during leg lifting. They ensure the stability of the pelvis, which is fundamental for proper leg alignment and balance. Without the proper functioning of these muscles, individuals can suffer from lower back, hip, or knee pains.
- Posture Maintenance: The glutes maintain pelvic alignment, which is critical for a healthy posture.
- Movement Facilitation: Each muscle contributes to various movements, such as squatting, jumping, and lateral movements, highlighting their importance in both everyday activities and athletic endeavors.
Nutrition and Diet for Building Muscle
When it comes to building muscle, particularly in the glutes, diet is as essential as the workout itself. Consuming the right macronutrients and sustaining a caloric surplus are key to fueling muscle growth.
Macronutrients and Calories
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle; they are critical for repair and growth. An individual should aim for high-quality protein sources like chicken, turkey, lean beef, and plant-based proteins such as beans and tofu. Carbohydrates provide the necessary energy for workouts and recovery. Opt for complex carbs like sweet potatoes, brown rice, and oatmeal. Fats should not be avoided as they’re vital for hormone production; however, one must choose healthy fats over saturated ones.
- Protein: Aim for about 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight daily for muscle gain.
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total daily calories should come from carbohydrates.
- Fats: 20-35% of daily calories are recommended to come from fats, focusing on healthy sources.
Healthy Fats and Muscle Growth
Healthy fats contribute significantly to muscle health by supporting cell structure and hormone function, which are essential for muscle growth. Including foods high in omega-3 fatty acids like fatty fish assists in reducing inflammation and promoting muscle recovery post-exercise. Avocados, nuts, and seeds are other excellent sources of healthy fats and can be easily included in a balanced diet to support muscle development.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Include fatty fish such as salmon or mackerel 2-3 times a week.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Use olive oil for cooking or dressings and snack on almonds or avocados.
Each meal should aim for a balance of the macro-nutrients, with an emphasis on adequate calorie intake to promote a caloric surplus, which is facilitating for muscle growth when combined with resistance training.
Basic Exercises for Glute Development
For anyone aiming to enhance their lower body, integrating squats, lunges, and bridges into a fitness routine targets the glute muscles effectively. These foundational movements are essential for glute development and offer a range of variations to suit different fitness levels and goals.
Squats and Variations
Squats are a powerhouse move for glute strengthening and can be performed with or without weights. To perform a squat:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Bend at the knees and hips, lowering the body as if sitting back into a chair.
- Keep the chest lifted and the weight in the heels.
- Push through the heels to return to the starting position.
For variety, incorporate squat variations such as the sumo squat, which emphasizes the inner thighs and glutes, or the pistol squat for a challenging single-leg exercise.
Lunges
Lunges are versatile and effective for targeting the glutes, hamstrings, and quads. Execute a basic lunge by:
- Stepping forward with one leg.
- Lowering the hips until both knees are bent at about a 90-degree angle.
- Keeping the front knee above the ankle and the back knee hovering above the ground.
- Pushing back to the starting position.
To progress, try walking lunges across the room or adding weights for resistance.
Bridges and Hip Thrusts
The glute bridge and its advanced cousin, the hip thrust, isolate and strengthen the glutes. Begin a glute bridge by:
- Lying flat on the back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Driving the heels into the ground, lifting the hips towards the ceiling while squeezing the glutes.
- Lowering the hips back down with control.
For a more intense workout, the hip thrust involves resting the upper back on a bench and can incorporate added weight for greater challenge. These exercises not only build muscle but also can improve posture and athletic performance.
Advanced Glute Training Techniques
To effectively enhance glute strength and aesthetics, adhering to advanced training principles is crucial. These include meticulous programming of progressive overload, incorporating a variety of exercises, and employing resistance training.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is paramount for ongoing muscular development. To apply this concept, one should progressively increase the resistance or volume over time. A practical method is to gradually add weight to staple compound movements like squats and deadlifts, ensuring that the body does not plateau but instead continues to build muscle.
Exercise Variation
Incorporating exercise variation is essential to target the gluteal muscles from different angles and to stimulate growth. For example, integrating movements such as Bulgarian split squats and barbell hip thrusts can activate different portions of the glutes more effectively than repetitive use of the same exercises.
Resistance Training
In the realm of resistance training, it’s not solely about lifting heavier weights. Utilizing bands for lateral walks or implementing leg press variations can be incredibly effective for challenging the muscles. Adequate resistance also applies to machine exercises like cable kickbacks, which are pivotal for those seeking to sculpt their glutes beyond basic bodyweight exercises.
Workout Routines and Programs
When embarking on a journey to enhance the glutes, individuals will come across a plethora of exercise routines and programs tailored to different fitness levels. These structured plans are designed to systematically target the muscles for optimal growth and toning.
Beginner Booty Building Routine
For beginners, it’s essential to start with a routine that focuses on foundational movements to build strength and muscle memory. An effective beginner program may include squats, lunges, and glute bridges performed three times a week. Emphasis should be on proper form and gradually increasing resistance to foster muscle growth without risking injury.
- Squats: 3 sets of 15 repetitions
- Lunges: 3 sets of 10 repetitions per leg
- Glute Bridges: 3 sets of 15 repetitions
These exercises ensure a solid base from which one can progress.
Intermediate Booty Building Program
Individuals with some experience in training their glutes can migrate towards an intermediate program that introduces more challenging movements and increased volume. They may include exercises like deadlifts, hip thrusts, and split squats. For intermediate trainees, routines usually incorporate the principle of progressive overload, advising them to increase weight or reps each week.
- Deadlifts: 4 sets of 8 repetitions
- Hip Thrusts: 4 sets of 12 repetitions
- Split Squats: 3 sets of 10 repetitions per leg
These exercises help sculpt the glutes by targeting different areas of the muscle group more intensely.
4 Week FitCrew by Ashley Lane App Challenge
A 4 Week FitCrew by Ashley Lane App is structured to systematically increase intensity and complexity of exercises over a four week period. This is an adequate time frame to see significant changes in muscle size and strength, provided that the individual follows the program with commitment and proper nutrition. Such a program is often split into phases, each with a specific focus like hypertrophy, strength, or power, to continuously challenge the muscles and encourage growth.
Try the FitCrew by Ashley Lane App for free for 7 days: 7 day free trial
Adherence to the 4-week plan not only increases glute size but also enhances overall lower body strength.
Recovery and Rest
Building a strong and shapely booty requires not just diligent training but also adequate recovery and rest. This balance is critical for allowing muscle fibers, including those in the glutes and hamstrings, to repair and grow.
Importance of Rest Days
Rest days are pivotal for muscle recovery. After strenuous workouts, the muscle fibers in the glutes and hamstrings endure microscopic tears and need time to repair. This is a natural process that leads to muscle strengthening and growth. Integrate at least 24 to 48 hours of rest before targeting the same muscle groups again to ensure full recovery and to prevent overtraining, which can hinder progress and increase the risk of injury.
Stretching and Mobility Work
In addition to rest days, stretching and mobility work play a significant role in a comprehensive recovery strategy. Stretching helps maintain flexibility, which can improve performance and decrease the risk of injury. Implement dynamic stretching before workouts to prepare the muscles and static stretching post-workout to aid in recovery. Mobility exercises, especially for the hip flexors and hamstrings, can further enhance the range of motion and promote efficient muscle function.
Accessories and Equipment
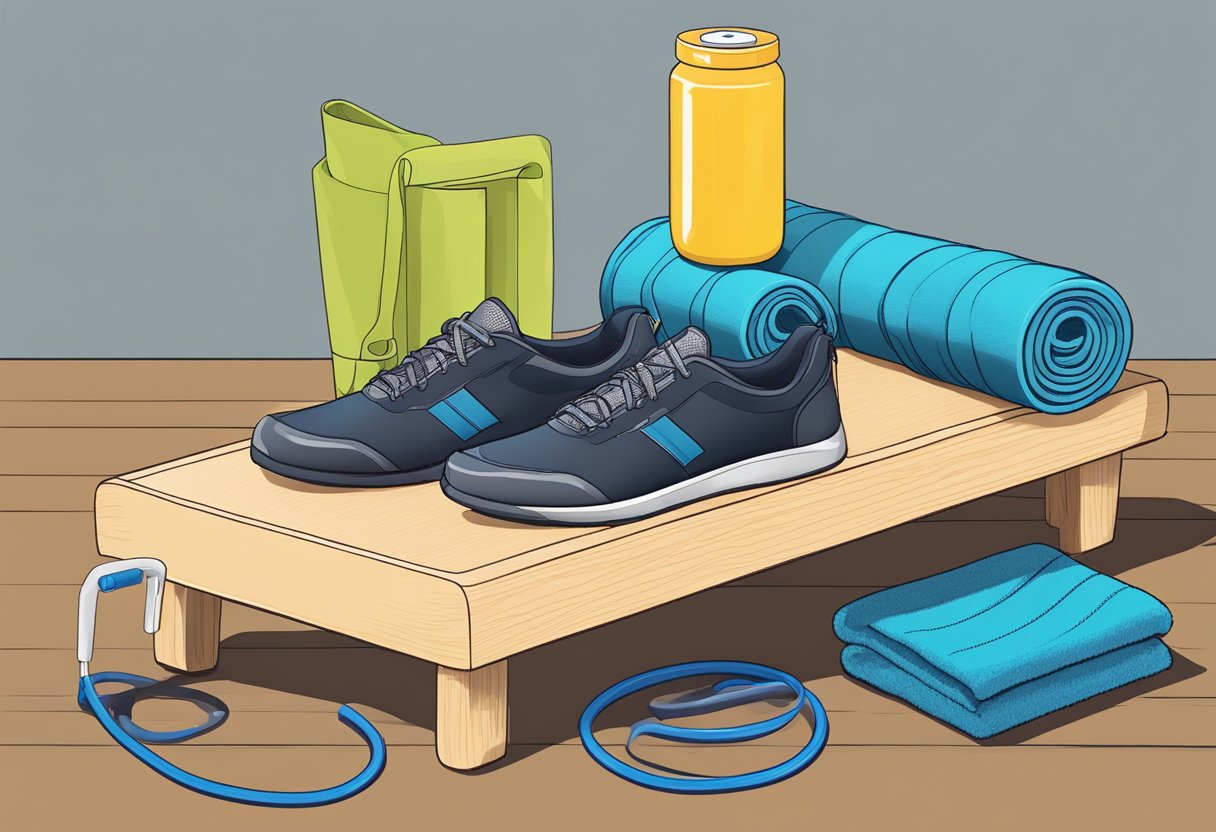

When building a booty, selecting the right accessories and equipment can be pivotal. It’s not just about what exercises one does, but also about how they leverage different tools to maximize muscle engagement and growth.
Using Weights
Weights such as dumbbells and kettlebells provide the resistance necessary to challenge the glute muscles. Effective exercises include Romanian deadlifts and weighted squats. For those starting out or looking to add variety, my recommendations for the best home equipment for growing your glutes are:Best way to start to workout from home
Bodyweight Exercises
Even without equipment, bodyweight exercises can be potent for building a booty. They focus on using one’s own body weight as resistance and often include movements like squats, lunges, and bridges. For those at home or with limited access to gym equipment, bodyweight exercises remain a crucial component.
Resistance Bands
Incorporating resistance bands can add a different level of challenge to booty-building workouts. They’re especially good for exercises like hip thrusts or lateral band walks. Fitness Project advises on the effectiveness of resistance bands for engaging the glutes during butt workouts.
Tips for Maximizing Results
Effective glute training is not just about the exercises you perform but also how you perform them. Mastery of form, understanding when to utilize compound movements, and fostering a strong mind-muscle connection can significantly enhance muscle building and the development of a stronger and larger booty.
Maintaining Proper Form
Maintaining correct form is crucial for targeting the glutes effectively and preventing injury. It ensures that each exercise maximizes glute activation while minimizing the involvement of unintended muscle groups. For example, when performing a squat, one should keep the chest up and the back straight, with the weight on the heels to fully engage the glutes.
Incorporating Compound Movements
Compound movements, such as squats and deadlifts, are foundational for building a robust lower body. They recruit multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to more calories burned and a greater stimulus for muscle growth. Integrating exercises like the walking lunges can add size to your glutes as part of a comprehensive muscle building regimen.
Mind-Muscle Connection
The mind-muscle connection is about focusing one’s awareness on the muscle being trained. By concentrating on squeezing the glutes at the top of movements like the glute bridge, individuals can enhance glute engagement and further stimulate muscle growth, leading to more effective workouts and better results.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the pursuit of enhancing glute size through exercise and lifestyle, certain questions frequently arise. This section aims to provide clear answers to those common inquiries.
What exercises are most effective for glute growth?
Exercises that focus on resistance work and progressive overload are most effective for glute growth. Squats, lunges, and deadlifts are staples in glute building routines.
Can certain foods help increase glute size?
To support muscle growth, including glute development, one’s diet should be rich in proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Nutrition is crucial for providing the energy and building blocks for muscle repair and growth.
What are the best strategies for building your glutes at home?
Building glutes at home can be accomplished with bodyweight exercises like squats, glute bridges, and lunges. Incorporating resistance bands or dumbbells can further enhance the effectiveness of a home workout.
How much time does it typically take to see changes in glute size?
Individual results may vary, but typically one might expect to see changes in glute size and shape within 4 to 6 weeks of consistent, targeted workouts and proper nutrition.
What gym workouts are optimal for enhancing glute size?
Gym workouts involving heavy weights and machines, like leg presses and hip thrusters, can be optimal for glute growing due to the ability to progressively overload the muscles over time.
Is it possible to see significant glute growth within a week?
Significant glute growth within a week is not typically realistic. Muscular development requires time, consistent training, and rest for recovery. Visible changes are more likely to be noticed over a longer period of consistent effort.


